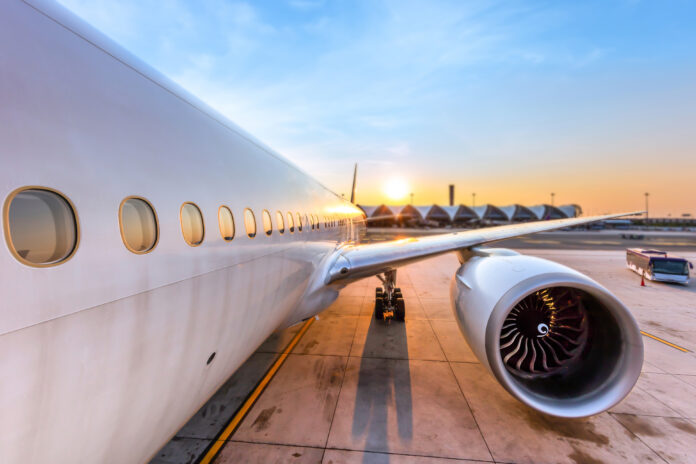
Aerospace engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with the design, construction, and science of aircraft and spacecraft.
It is a highly specialized field that combines elements of mechanical, electrical, and materials engineering.
Aerospace engineers are at the forefront of developing new technologies that can push the boundaries of what is possible.
From developing new propulsion systems to designing more fuel-efficient aircraft, they are constantly innovating to make air and space travel more safe, efficient, and sustainable.
The aerospace industry is one of the most fascinating and rapidly-changing industries in the world.
With new advances in technology, there are always new challenges and opportunities for aerospace engineers to explore.
If you’re interested in learning more about this exciting field, read on for an introduction to aerospace engineering.
What is aerospace engineering?
Aerospace engineering is the process of designing, building, and testing aircraft, missiles, and spacecraft.
Aerospace engineers are responsible for the safety and performance of these vehicles, which means they must have a deep understanding of aerodynamics, propulsion, and materials science.
They also need to be able to work with complex computer models in order to design efficient and safe vehicles.
In addition to their technical skills, aerospace engineers must also be able to communicate effectively and work well in teams.
With the ever-increasing demand for faster and more efficient travel, there is a great need for talented aerospace engineers.
Those who choose this career can take pride in knowing that they are helping to shape the future of flight.
The history of aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is a relatively young field, with its origins dating back to the early days of powered flight.
The Wright brothers are often credited as being the pioneers of aerospace engineering, as they were the first to successfully fly a powered aircraft.
However, the field really began to take off in the years leading up to World War II.
With the threat of war on the horizon, both the United States and Nazi Germany began investing heavily in aeronautical research and development.
This led to rapid advancements in the field, and by the time the war began, both sides had access to a variety of sophisticated aircraft.
In the aftermath of the war, aerospace engineering continued to evolve at a rapid pace.
The Space Race between the US and USSR spurred even greater innovation, and by the end of the 20th century, aerospace engineering had reached a level of sophistication that would have been unthinkable just a few decades earlier.
Today, aerospace engineering remains an essential part of our world, and its future looks brighter than ever.
The role of aerospace engineers
Aerospace engineers are responsible for designing, building, and testing aircraft, spacecraft, missiles, and rockets.
They typically specialize in one type of vehicle, such as commercial airplanes or military fighter jets.
In recent years, the role of aerospace engineer has expanded to include the design of drones and other unmanned aerial vehicles.
Aerospace engineers must have a strong understanding of physics and mathematics, and they must be able to use various computer-aided design (CAD) tools.
The most successful aerospace engineers are those who are able to think creatively and solve problems effectively.
The future of aerospace engineering
The future of aerospace engineering is both exciting and uncertain.
On the one hand, recent advancements in 3D printing and other technologies are making it possible to build lighter and more efficient aircraft.
In addition, electric propulsion systems are becoming increasingly viable, promising to revolutionize the aviation industry.
On the other hand, the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic are still unknown, and it is possible that the aerospace industry will experience a prolonged downturn.
Despite these challenges, there is reason to be optimistic about the future of aerospace engineering.
As new technologies continue to emerge, it is likely that the aerospace industry will undergo a period of transformation and renewal.
The result will be a more sustainable and efficient aviation sector that can meet the needs of a rapidly growing global population.